How to Find the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
The surface area of a rectangular prism is a crucial concept in geometry that has various applications in real life, from packaging design to architectural planning. Understanding how to find the surface area effectively can enhance comprehension in the field of mathematics and practical problem-solving. In this article, we will explore the surface area calculation for a rectangular prism, break down the rectangular prism surface area formula, and guide you through the steps to calculate it using various dimensions.
Understanding the Surface Area Formula
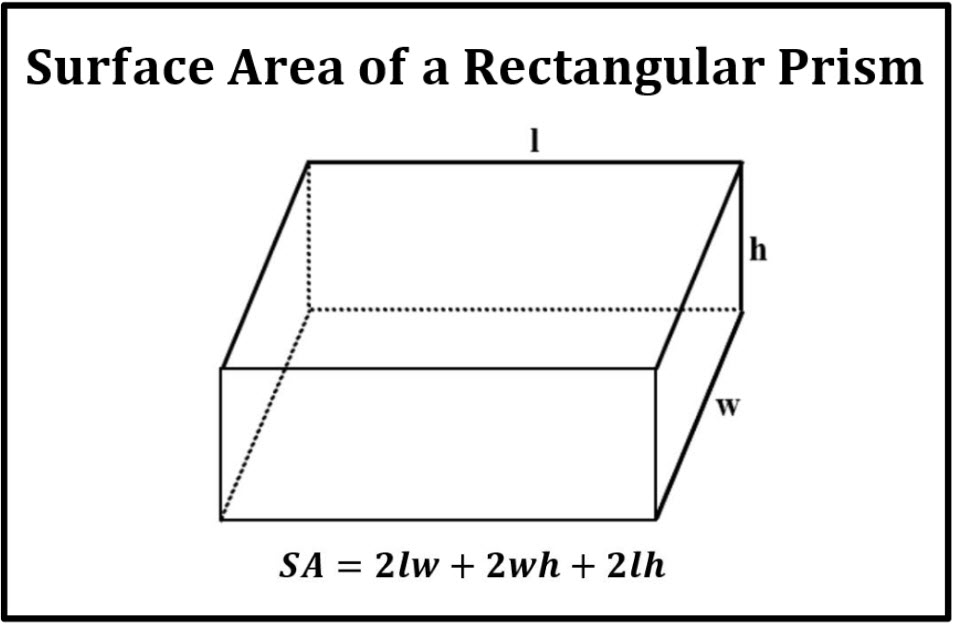
The surface area of a rectangular prism involves calculating the area of all six faces, which are made up of pairs of rectangles. To better understand the **surface area formula**, the primary equation is derived as follows: the formula for finding the surface area of a rectangular prism is given by:
Surface Area = 2(lw + lh + wh), where l is the length, w is the width, and h is the height of the prism. This formula combines the area of each face, providing a total surface area measurement.
Breaking Down the Formula Components
When applying the surface area formula, it’s important to recognize the contributions of each face of the prism. Each dimension impacts the **total surface area** significantly. First, we calculate the base and top face areas using the formula for the area of a rectangle: Area = length × width. This gives us 2(lw). Next, the front and back faces are calculated as 2(lh), and lastly, the side faces contribute 2(wh). This comprehensive approach ensures that every surface is accounted for when performing your **calculations for 3D shapes**.
Practical Example of Surface Area Calculation
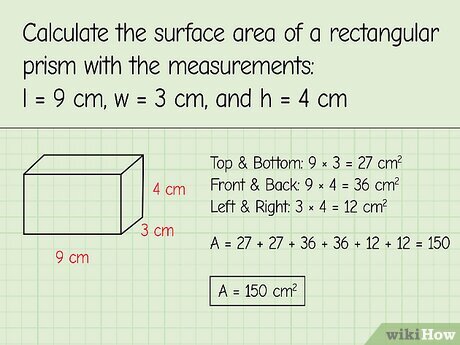
Let’s consider an example: suppose we have a rectangular prism with a length of 5 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 4 cm. To find the **surface area of this rectangular prism**, we can use the surface area formula introduced earlier. Plugging these dimensions into the formula provides:
Surface Area = 2(5*3 + 5*4 + 3*4) = 2(15 + 20 + 12) = 2(47) = 94 cm². Thus, the **calculations in geometry** yield a surface area measurement of 94 square centimeters, which emphasizes the practicality of understanding how to find the surface area.
Visualizing Rectangular Prisms for Better Understanding
Visual aids can greatly enhance the understanding of how to find the surface area. Utilizing diagrams or 3D models can make distinguishing between the different faces of a prism easier. In educational contexts, employing illustrations of prism surfaces can foster better **comprehension** and engagement among students. Applying **visual representation of area**, along with concrete examples, boosts retention of geometric principles and assists learners in grasping complex calculations.
Educational Geometry and Real-World Applications
Learning about the **surface area** has significant real-world applications, particularly in fields such as architecture, engineering, and packaging. For example, understanding **surface calculations in physics** enables designers to create structures that optimize materials, directly affecting cost and efficiency. In educational settings, students can deepen their knowledge by conducting experiments that involve measuring the surface area of everyday objects, thus linking theoretical principles to **practical math applications for surface area**.
Common Mistakes in Surface Area Calculations
Many students encounter challenges when calculating the surface area of a rectangular prism. Common errors often involve neglecting to account for all faces of the prism, or miscalculating the dimensions of each rectangle. It’s imperative to emphasize clarity in teaching these calculations, reinforcing the **)importance of surface area** measurement** early in the education process. Regular practice through **surface area exercises** and worksheets can uncover potential misconceptions and enhance overall proficiency.
Steps to Calculate the Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms
Determining the surface area of a rectangular prism can be simplified into clear, actionable steps. To streamline this **calculation process**, follow these guidelines:
- Identify the dimensions: Gather the prism’s length, width, and height.
- Apply the surface area formula: Use the formula to compute the surface area based on the gathered dimensions.
- Consider unit consistency: Ensure that all dimensions are in the same unit to maintain clarity in your **surface area measurement**.
- Cross-verify calculations: Double-check each step to prevent common errors that might arise during calculations.
By following these steps diligently, individuals can gain confidence while **finding the surface area** and can greatly improve their **understanding of surfaces**.
Key Takeaways
- The formula for finding the surface area of a rectangular prism is 2(lw + lh + wh).
- Visual aids are critical for comprehending geometric concepts and improving student engagement.
- Real-world applications demonstrate the versatility of surface area calculations beyond mere academic exercises.
- Practice is vital for mastering the method of calculating surface area and avoiding common mistakes.
FAQ
1. What is the importance of knowing the surface area of a rectangular prism?
Understanding the surface area of a rectangular prism is crucial as it allows various fields, including construction and manufacturing, to determine material needs, optimize costs, and improve design efficiencies. For example, certificates in **educational geometry** highlight the relevance of these skills in practical applications.
2. Can the surface area formula be applied to other geometric shapes?
Yes, while the surface area formula concerning the rectangular prism is specific to its dimensions, similar principles can be used to find the area in other geometric shapes. Many geometric solids utilize formulas that certainly correspond with the rectangular prism surface area via mathematical modeling.
3. How do I ensure I am using the correct units when measuring surface area?
To ensure that all measurements correlate properly, it’s essential to convert all length measurements into the same unit (e.g., all inches or all centimeters). Consistency is vital in ¬**calculations for surface area** in geometry, keeping total area properly expressed in units like square inches or square centimeters.
4. How can real-life contexts improve surface area learning?
Engaging students with real-life examples, like measuring the surface area of boxes or containers, greatly enhances their understanding and retention of concepts. Applying surface area formulas to practical tasks encourages critical thinking while cementing the learning within familiar contexts.
5. What tools can help in surface area calculations?
Graphing calculators, software, or online tools can assist in surface area calculations. Many educational platforms provide **surface area worksheets** and interactive simulations that can support the learning process, enabling students to practice and refine their skills effectively.