“`html
How to Effectively Find Marginal Cost in 2025
Understanding how to find **marginal cost** is essential for making informed financial decisions in any business. Marginal cost refers to the additional cost incurred for producing one more unit of a product. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the **marginal cost formula**, its significance in business strategies, and techniques for effective **marginal cost analysis** in 2025.
Understanding Marginal Cost Definition
Before we explore how to calculate marginal cost, it’s crucial to grasp its meaning. **Marginal cost** is defined as the change in total cost that comes from producing one additional unit of a product. This concept is integral in economics, helping businesses optimize their production levels. The formula used to determine **marginal cost** is:
Marginal Cost = Change in Total Cost / Change in Quantity Produced
This formula allows businesses to identify how much extra they need to spend to increase production. Understanding this definition will form the basis of our comprehensive analysis.
The Importance of Marginal Cost in Business
Understanding the importance of **marginal cost** is vital for businesses aiming to maximize profit. By evaluating **marginal cost** and **average cost**, companies can determine the optimal production level where the revenue generated is maximized while costs are minimized. Analyzing **marginal cost** helps in making informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, resource allocation, and production efficiency.
Examples of Marginal Cost
To illustrate **marginal cost**, consider a bakery that produces cakes. If the total cost of producing 10 cakes is $200, and the cost for 11 cakes rises to $210, the **marginal cost** of producing the 11th cake would be $10. This example demonstrates how businesses can assess costs on a unit-by-unit basis to improve **cost analysis** and profit maximization strategies.
Calculating Marginal Cost: Step-by-Step Guide
Identifying marginal cost involves several steps: first, collect data on total costs and production levels. Next, apply the **marginal cost formula** by finding the difference in total costs at two production levels. Lastly, analyze the results to make decisions on production adjustments or price changes. This systematic approach to **determining marginal cost** is essential for accurate **marginal cost analysis**.
Marginal Cost Analysis in Different Business Scenarios
Different industries may face unique challenges and opportunities when analyzing marginal cost. Understanding these nuances aids in developing effective pricing strategies and production plans.
Marginal Cost in the Manufacturing Sector
In manufacturing, companies often encounter **marginal cost** structures that significantly influence production decisions. Manufacturers must assess both **fixed costs** and **variable costs** to establish a comprehensive production budget. Marginal cost considerations can help in determining how many units should be produced to maintain profitability and operational efficiency.
Marginal Cost and Revenue Considerations
The relationship between **marginal cost** and revenue is crucial for establishing effective pricing strategies. If the revenue from selling an additional unit exceeds the **marginal cost** of production, it is beneficial to produce more. Conversely, if the **marginal cost** surpasses the revenue generated, it indicates a need for cost reduction or an adjustment in production output.
Changes in Marginal Cost and Its Implications
Businesses must be cognizant of how **changes in marginal cost** can influence their operations. For example, a rise in raw material prices can lead to increased **marginal cost**, necessitating re-evaluation of pricing strategies. Analyzing these fluctuations allows businesses to remain competitive while ensuring they maximize profitability.
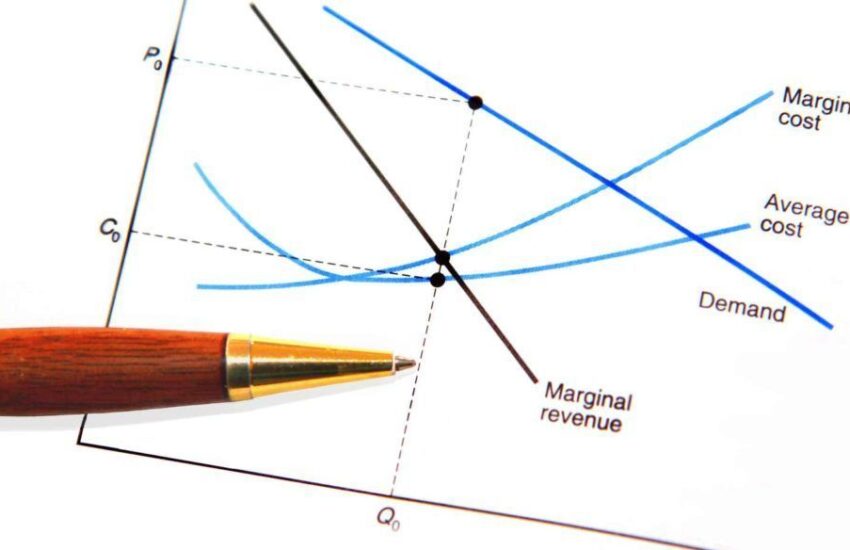
Understanding Marginal Cost Curves
Creating a visual representation of **marginal cost** can provide deeper insights into production decisions and enable businesses to grasp their cost behaviors more effectively. The **marginal cost curve** is a powerful tool that depicts how marginal costs change with varying levels of output.
Creating and Analyzing the Marginal Cost Graph
The **marginal cost graph** represents the relationship between output levels and **marginal cost** incurred. Typically, the graph shows a U-shaped curve, reflecting diminishing marginal returns at higher levels of production. This illustration can help businesses identify the most cost-efficient production level.
Marginal Cost vs Average Cost: Key Differences
While comparing **marginal cost** and **average cost** is essential for accurate financial analysis, it is crucial to understand the key differences. **Average cost** is calculated by taking total costs divided by the number of goods produced, while **marginal cost** focuses only on the cost incurred by producing one additional unit. Analyzing both allows firms to improve financial metrics significantly and make informed **pricing decisions**.
Long-Run vs Short-Run Marginal Cost
Businesses should differentiate between **short-run marginal cost** and **long-run marginal cost**. Short-run costs assume some factors are fixed, whereas long-run costs consider all variables flexible over time. Understanding which marginal cost measure applies in various situations allows businesses to strategically plan their operations and adjust their production dynamics accordingly.
Key Takeaways
- **Marginal cost** is vital in determining optimal production levels and pricing strategies.
- Understanding **marginal cost implications** helps businesses navigate economic fluctuations and market dynamics.
- Utilizing the **marginal cost formula** can improve financial decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Recognizing the differences between **marginal cost** and average cost enhances financial analysis.
FAQ
1. What is the marginal cost meaning in economics?
In economics, **marginal cost** is defined as the increase in total cost that arises from producing one additional unit of a good or service. It helps businesses determine the optimal output level for maximizing profits, guiding production and pricing strategies.
2. How do shifts in marginal cost affect production decisions?
Shifts in **marginal cost** can significantly impact production decisions. For example, if marginal costs increase due to rising raw material prices, companies may decide to reduce output or increase prices to maintain profitability. Analyzing these fluctuations in marginal costs is crucial for strategic planning.
3. Can you provide an example of marginal cost in production?
Certainly! Suppose a factory produces 100 gadgets at a total cost of $1,000. If producing one more gadget increases the total cost to $1,025, the **marginal cost** for that additional gadget is $25. This example illustrates how companies can use marginal cost to inform their production processes.
4. What is the significance of marginal cost in business strategy?
The significance of **marginal cost** in business strategy lies in its ability to inform pricing and production levels that maximize profit. By calculating marginal costs, businesses can adjust policies and optimize operations to enhance efficiency and competitiveness in the market.
5. How does marginal cost relate to supply?
There is a direct relationship between **marginal cost** and supply in economics. Typically, as marginal costs increase, the quantity supplied may decrease, leading to higher prices for consumers. Understanding this relationship helps businesses align their supply strategies with cost structures effectively.
“`