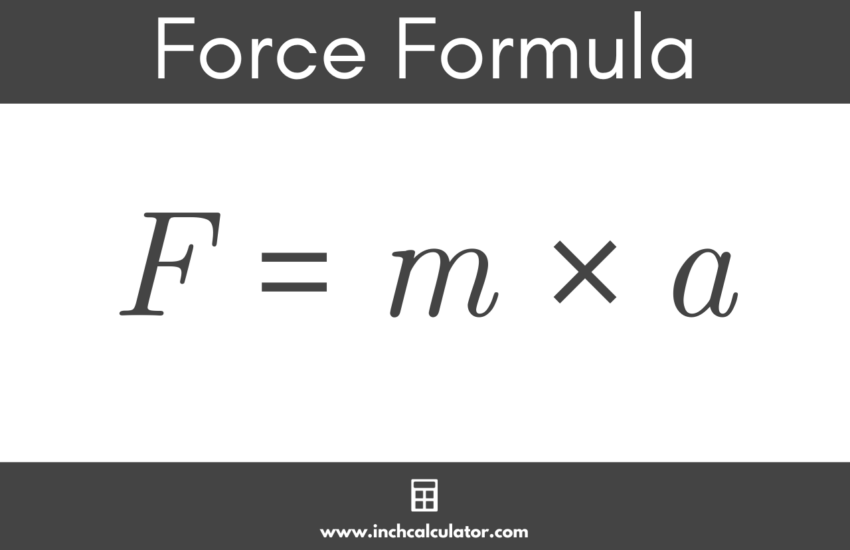“`html
How to Properly Calculate Force: The Ultimate 2025 Guide to Understanding Physics
Welcome to the ultimate guide on force calculation! In this article, we will explore the basic concepts of force, how it relates to mass and acceleration, and provide practical examples of calculating force in various scenarios. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or just curious about physics, this guide aims to explain the intricacies of force and how to calculate it properly!
The Fundamentals of Force in Physics
Understanding the basics of force is essential in the field of physics. Force is defined as an interaction that changes an object’s motion, typically described in terms of mass and acceleration. The fundamental theorem governing force is Newton’s Second Law, which states: Force = Mass × Acceleration (F = m × a). This relationship highlights how the application of force can impact an object’s motion through the principles of mechanics and dynamics.
Different Types of Forces
Forces can be categorized into two main types: contact forces and non-contact forces. Contact forces occur when objects are in physical contact, such as friction, tension, and normal force. For example, when you push a book across a table, the force exerted by your hand is a contact force. On the other hand, non-contact forces include gravitational force and electromagnetic force, which can act at a distance. Understanding these categories is crucial for correctly applying force concepts in various situations.
Units of Force Measurement
The standard unit of force is the Newton (N), named after Sir Isaac Newton. One Newton can be defined as the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at the rate of one meter per second squared (1 N = 1 kg·m/s²). In different scenarios, especially in engineering or sports, it is also essential to understand and convert between different units of force such as pounds (lbs) or dynes. Accuracy in force measurement ensures reliable calculations in practical applications.
Force Calculation Examples in Everyday Life
There are numerous scenarios where understanding how to calculate force is essential in our daily life. For example, when climbing stairs, your body applies a force against gravity, which can be quantified to understand the energy expenditure involved. Another example is in automotive design—calculating forces acting on a vehicle during acceleration or deceleration is crucial for safety and performance. By applying the principles of the force calculation throughout these situations, you can gain insight into not just physics, but practical applications that impact your life.
Understanding Forces through Free Body Diagrams
Free body diagrams are invaluable tools for visualizing forces acting on an object. By representing the object as a dot and drawing arrows to signify all the acting forces, one can analyze the net force on that object. This method combines both static and dynamics concepts, making it easier to solve for unknown forces or derive equations related to motion.
Drawing a Free Body Diagram
To draw a free body diagram, start by identifying the object of interest. Then, determine all forces acting on it, including gravitational force, normal force, and any applied forces. Each force should be represented as an arrow: the length indicates the force’s magnitude, while the direction shows the force’s application. For instance, if a box rests on a table, you would draw an arrow pointing downwards representing the force of gravity, and another arrow pointing upwards for the normal force. By setting these forces in relation to one another, you’ll gain clarity about how they affect motion.
Net Force and Motion
The net force is the vector sum of all individual forces acting on an object. If multiple forces act on an object in different directions, it is critical to break them down into their components to get an accurate reading of motion. For example, if a force of 10 N acts to the right and 4 N acts to the left, the net force is 6 N to the right. This concept is pivotal in understanding how forces lead to changes in motion under Newton’s laws of motion.
The Role of Force in Dynamic Scenarios
In dynamic situations, such as collisions and projectile motion, force plays a significant role in determining outcomes. Understanding these interactions helps in areas as diverse as vehicle safety designs, sports science, and aerospace engineering.
Calculating Force in Collisions
To analyze collisions, we often use the concept of impulse, which relates the change in momentum to the force applied over a specific period of time. By using the impulse-momentum theorem, you can calculate forces involved during impact events, such as car accidents. For instance, in a car crash scenario, measuring the changing speeds of vehicles before and after the collision allows engineers to estimate the forces involved and improve safety features in vehicles.
Projectile Motion and the Force of Gravity
When objects are thrown or projected, their motion can be analyzed under the influence of external forces, particularly gravity. To calculate the force exerted by gravity on an object, use the formula: Weight = Mass × Acceleration due to Gravity (W = mg). The standard acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.81 m/s² on Earth. For basketball players, understanding gravitational force can enhance techniques in shooting and jumping for rebounds.
Applications of Force in Various Fields
The application of force is widely encountered across numerous fields including engineering, sports, and fluid dynamics. Understanding how force interacts with different materials and systems allows professionals to innovate solutions that rely on these fundamental principles.
Forces in Engineering
In engineering, understanding force is crucial for building structures, machinery, and products that can withstand various loads and ensure reliability. Engineers calculate forces to assess safety factors and establish whether materials can handle inferred stresses. By using force equations or simulating scenarios, they can better predict the responses of structures to dynamic loads.
Force in Sports Science
Sports science utilizes knowledge of force and motion to enhance athletic performance through training and technique optimization. Coaches and trainers assess athletes’ movements and the forces at play, ensuring strategies are used to minimize inefficiencies and maximize effectiveness. For example, sprinters use force vectors to determine optimal running techniques and improve acceleration.
Key Takeaways
- Force is a fundamental aspect of physics defined by mass and acceleration.
- Understanding types of forces and their applications is critical in physics, engineering, and everyday life.
- Free body diagrams and net force calculations are essential tools for analyzing motion.
- Real-world applications of force calculations can significantly improve safety, efficiency, and performance.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between contact and non-contact forces?
Contact forces occur through physical interaction between objects, such as friction and tension, whereas non-contact forces act across distances, like gravitational and electromagnetic forces. Understanding the difference helps in analyzing various physical scenarios effectively.
2. How can I calculate force accurately in my experiments?
To calculate force accurately, ensure you measure the mass and acceleration precisely. Using a force meter or a similar tool can improve consistency in measurements. Always double-check calculations using the formula: Forced = Mass × Acceleration.
3. What are common mistakes in force calculations?
A common mistake is neglecting the effect of unbalanced forces acting in opposite directions rather than summing them up properly. Misunderstanding the role of equilibrium can also lead to calculation errors, as it may alter how forces interact.
4. Why is Newton’s Second Law significant in understanding force?
Newton’s Second Law: F = ma is fundamental to understanding how force relates to motion. It helps physicists and engineers anticipate an object’s behavior under different forces and is applicable in various fields, from automotive safety to athletic performance.
5. How does force apply to real-world applications?
Force calculations influence numerous real-world applications such as designing safer vehicles, creating better sports equipment, and understanding structural integrity in engineering. Awareness of force promotes innovation and improvements across various industries.
6. Can I visualize forces using diagrams?
Yes, diagrams like free body diagrams are excellent for visualizing forces acting on an object. They simplify complex interactions into clearer representations, making it easier to understand the net force and overall implications.
7. Is it important to consider friction in force calculations?
Absolutely! Friction significantly affects motion and stability. When calculating force, it’s vital to account for the friction acting between surfaces, especially in practical applications where energy loss may occur.
“`