“`html
Effective Ways to Calculate Consumer Surplus: Understand Market Benefits in 2025
Understanding Consumer Surplus
Consumer surplus is a crucial concept in economic theory that provides significant insights into consumer welfare. It represents the difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and what they actually pay. Understanding how to calculate consumer surplus enables stakeholders to analyze the benefits consumers receive in various market conditions. In this article, we will dive deep into the mechanisms of consumer surplus, relevant formulas, and practical applications in 2025.
What is Consumer Surplus?
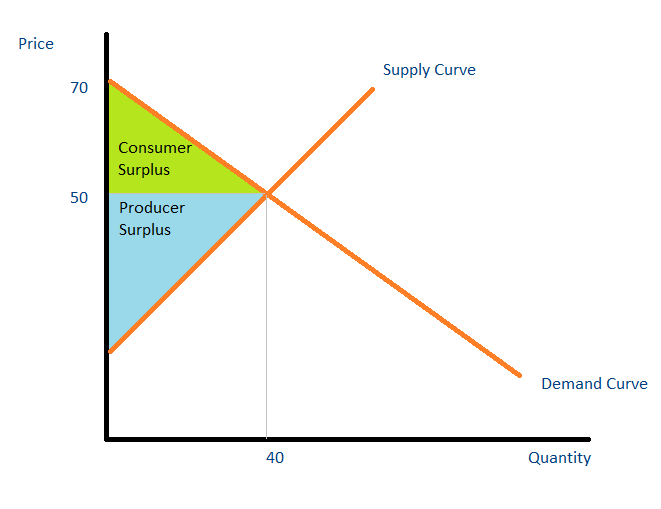
Consumer surplus is an indicator of the economic advantage consumers obtain when they pay less than what they are willing to pay. This surplus is visually represented in a consumer surplus graph, wherein the area above the market price and below the demand curve depicts the surplus. It reflects the utility consumers derive from goods, suggesting a higher consumer satisfaction. For example, if a consumer is willing to pay $100 for a concert ticket but buys it for $70, their consumer surplus is $30. This concept highlights the benefits of consumer surplus in assessing market efficiency and consumer behavior.
The Importance of Consumer Surplus
Consumer surplus plays a vital role in welfare economics, aiding economists in understanding market dynamics and consumer choices. By evaluating the total economic surplus, including both consumer and producer surpluses, we attain a comprehensive view of market health. Understanding shifts in demand and supply and their effect on consumer surplus can assist in price determination strategies for businesses and policymakers. Moreover, a rise in consumer surplus often leads to increased consumer spending, amplifying overall economic growth.
How to Calculate Consumer Surplus
The calculation of consumer surplus can be straightforward when understood correctly. The basic formula is:
Consumer Surplus = Willingness to Pay – Market Price.
However, a more involved approach often includes graphical representation using the area of triangles formed from the demand curve and market price.
For examples, if a large number of consumers are willing to pay different prices for the same product, the respective individual surpluses can be aggregated to find the aggregate consumer surplus. This calculated total provides insight into consumer behavior on a broader scale, helping businesses tailor their pricing strategies.
The Role of Market Equilibrium
The relationship between demand and supply determines market equilibrium and profoundly affects consumer behavior. When analyzing market demand and supply curves, understanding where they intersect—the equilibrium price—is essential for measuring consumer surplus. Any shifts either in the supply or demand can significantly alter the equilibrium price, impacting overall consumer welfare.
Understanding Equilibrium Price
The equilibrium price is where the quantity of goods demanded equals the quantity supplied. At this price, the economy achieves maximum efficiency, and consumer surplus is optimally portrayed. Suppose the demand for a product increases due to a shift in consumer preferences, leading to higher prices without a corresponding increase in supply. In that case, the consumer surplus may decrease, highlighting that changes in price affect consumer price sensitivity.
Effects of Price Changes on Consumer Surplus
Price fluctuations can drastically impact consumer surplus. For instance, if prices decrease due to increased supply, consumers experience a larger surplus since they are paying less for the same utility. This scenario indicates positive welfare implications for consumers and can stimulate further economic activity through greater consumer savings. Monitoring these effects helps businesses develop strategic pricing models that maximize total surplus.
Real-World Examples of Consumer Surplus in Action
A practical example can illustrate how consumer surplus functions in real-world scenarios. Consider a company that introduces a new technology product priced competitively at $300 while customers express a willingness to pay up to $500. The consumer surplus per unit sold is $200. If the company’s marketing efforts result in a substantial increase in demand, the resultant price adjustments and shifts in supply may either optimize or diminish consumer surplus, providing an ongoing analysis challenge for both economic policies and market strategies.
Surplus Measurement: Key Techniques
The measurement of consumer surplus requires a nuanced understanding of various analytical tools and methodologies. Techniques differ considerably based on product and market types, but there are fundamental approaches that work effectively across economic landscapes.
Valuation Techniques for Surplus Measurement
One effective method is through conducting surveys to gauge consumer willingness to pay, which contributes to a more accurate surplus measurement. Additionally, price comparison between different sellers can reveal variances in surplus generated across market segments. In specific cases, understanding how price discrimination effects contribute to consumer surplus may help refine pricing strategies further to benefit the wider consumer base.
Quantitative Assessment of Consumer Behavior
Analysts often leverage statistical modeling and data analysis to understand the dynamics of consumer surplus and behaviors. Market analysis tools can track demand shifts and consumer preferences, allowing businesses to forecast their potential adjustment effectively in line with consumer trends. Analyzing these factors can provide insights into a business’s future growth trajectory by emphasizing its role in preserving or enhancing consumer surplus.
Government Policies and Economic Impact
Government interventions often play a critical role in shaping consumer surplus through regulatory measures and tax policies. By imposing fair trade practices and price controls, governments can influence market balances leading to improved consumer protection and subsequently greater consumer surplus. Effective policies can transform market landscapes, creating opportunities for increased utility and consumer welfare.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding consumer surplus is crucial to analyzing consumer welfare and market efficiency.
- Consumer surplus can be calculated using basic formulas or graphical methods illustrating demand and supply curves.
- Market equilibrium greatly influences levels of consumer surplus experienced in economic transactions.
- Monitoring price changes allows businesses to anticipate shifts in consumer surplus effectively.
- Government policies significantly affect the consumer landscape, impacting surplus measurement and analysis.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of consumer surplus in market analysis?
Consumer surplus is significant as it provides insight into consumer behavior, indicating the economic benefits consumers gain in a market. It’s essential for assessing market efficiency and understanding how pricing strategies can influence economic policies.
2. How does demand elasticity affect consumer surplus?
Demand elasticity indicates how sensitive consumer demand is to price changes. Higher elasticity means that small changes in prices can lead to large shifts in quantity demanded, thus affecting the overall consumer surplus available in the market.
3. Can consumer surplus be impacted by government regulations?
Yes, government regulations can influence consumer surplus by implementing pricing controls, taxes, or subsidies. These regulations can enhance or restrict consumer welfare by shifting supply and altering market conditions.
4. What tools can be used for consumer surplus analysis?
Analysts can use various tools for consumer surplus analysis such as surveys, market data analysis, and economic modeling. These methodologies provide a clearer picture of consumer preferences and their impact on market efficiency.
5. How can understanding consumer surplus influence marketing strategies?
Understanding consumer surplus allows businesses to tailor their pricing strategies effectively, ensuring they maximize aggregate consumer surplus. This targeted approach not only enhances consumer satisfaction but fosters brand loyalty and encourages expenditure.
“`