Mastering Synthetic Division: Essential Strategies for 2025
Synthetic division is a key method used in algebra for simplifying the process of dividing polynomials, especially when working with linear divisors. Unlike traditional long division, this technique employs a streamlined approach, making it an essential skill for students and professionals in mathematics. This article highlights effective ways to master **synthetic division**, ensuring a strong foundation in polynomial division and related concepts for 2025.
Understanding Synthetic Division
To fully grasp **synthetic division**, it’s crucial to understand its foundational components. This method works with a **dividend**, which is the polynomial being divided, and a **divisor**, which is the polynomial we are dividing by. The coefficients of these polynomials come directly into play. When a linear divisor is involved, synthetic division can simplify the process significantly. This is particularly useful for evaluating polynomials and larger polynomial expressions.
The Process of Synthetic Division
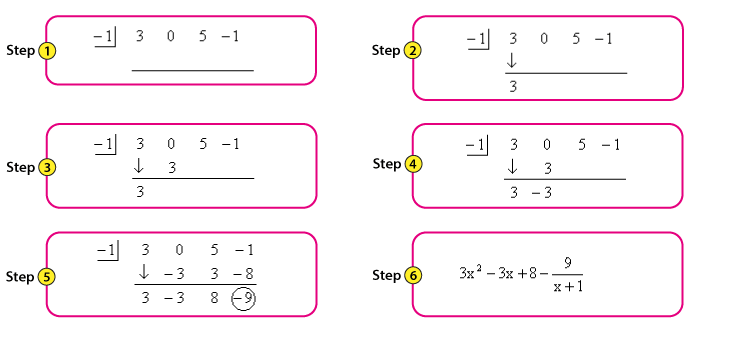
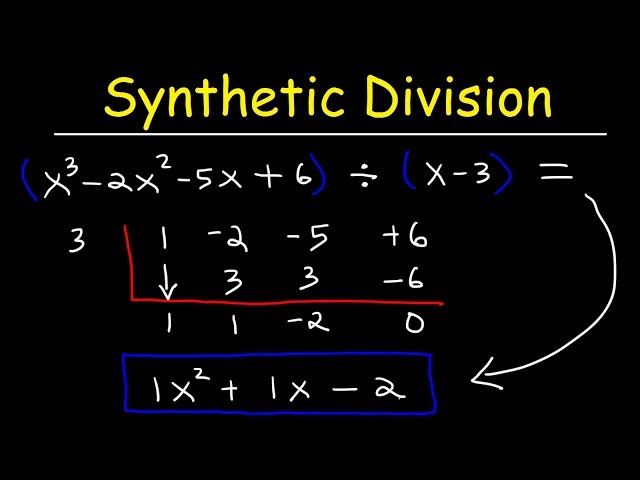
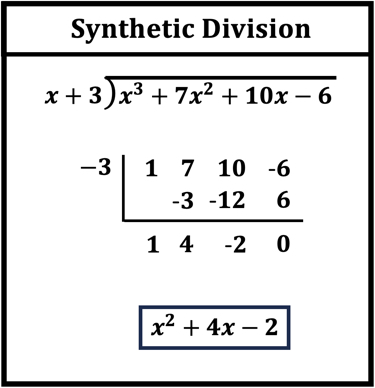
Let’s explore the **synthetic division steps** to understand how to effectively apply this technique. First, write down the coefficients of the dividend. Next, substitute the zero of the divisor. After that, bring down the leading coefficient and perform a series of multiplying and adding operations. This technique minimizes errors and allows students to calculate the **remainder** and **quotient** efficiently. Once you understand how to set up this method, it will be easier to execute further algebraic manipulation and identify **polynomial roots**.
Advantages Over Long Division
When comparing synthetic division to long division, many students find synthetic division to be more efficient and straightforward. The quick calculations allow for easier management of polynomials, especially of higher degrees. Instead of working through multiple steps in long division, synthetic division reduces operations by eliminating variables until you reach a more simplified form. The trade-off is recognizing when to apply synthetic division effectively—once you learn to do so, it can significantly improve your **algebra skills**.
Practice Problems for Mastery
To truly master synthetic division, working through practice problems is essential. Educational resources present numerous **practice problems** where you can divide polynomials of varying degree. By consistently practicing, learners can **calculate easily** and reinforce these skills. Group study sessions can also be beneficial, allowing peers to compare methods and validate their understanding of synthetic division. Regular practice, coupled with instructional support, will lead to greater retention and application of **polynomial evaluation techniques**.
Applications of Synthetic Division
Synthetic division isn’t just an academic exercise; it has real-world applications in fields such as engineering, economics, and data analysis. By understanding its practical uses, students can appreciate its value beyond the classroom. For instance, one can use synthetic division to assess various **rational functions** within broader mathematical models. This understanding is pivotal in reducing complex problems to solvable forms, particularly when dealing with **polynomial functions** in professional settings.
Evaluating Polynomial Functions
One key application of synthetic division is in the evaluation of polynomial functions at specified values. Using synthetic substitution, you can determine how a polynomial behaves or its value over specific intervals. This method simplifies the evaluation process significantly and is vital in decision-making processes across various scientific fields. Students should frequently **evaluate polynomials** with synthetic division to increase their comfort in applying the technique efficiently.
Exploring Polynomial Roots through Synthetic Division
Another significant application is finding the **roots** of polynomials. When you apply synthetic division, you can systematically test potential zeros and identify which values lead to a remainder of zero. This allows for a thorough exploration of polynomial roots, further enhancing understanding in algebra. Mastery of finding roots not only helps in synthetic division but also fortifies problem-solving techniques across other related areas in mathematics.
Understanding the Remainder Theorem
The remainder theorem offers crucial insight into polynomial behavior when combined with synthetic division. It states that when you divide a polynomial \(P(x)\) by \(x-c\), the remainder is simply \(P(c)\). This implies that synthetic division can be efficiently employed to find not only the **remainder** but also ascertain polynomial **roots**. Including the remainder theorem in the study of synthetic division reinforces overall comprehension of polynomial operations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While mastering synthetic division, it’s essential to be aware of common pitfalls that can hinder understanding. One significant mistake is misplacing coefficients or neglecting to align them correctly with corresponding terms, leading to incorrect results. Another frequent error is miscalculating the final **remainder**, which can result in a cascading effect on the identified quotient. By paying close attention to detail and systematically following **synthetic division steps**, learners can avoid these errors.
Importance of Coefficients and Alignment
Coefficients play a central role in the division process. Correctly identifying and aligning coefficients of the polynomial is paramount. Many students struggle with negative coefficients, so it’s beneficial to practice through differentiated problems that incorporate various **numerical coefficients**. Create a reference guide that highlights common errors as well as tips for keeping equations in order, which will ultimately enhance syntactical accuracy in polynomial manipulations.
Real-World Examples of Synthetic Division
Integrating real-world examples of synthetic division can aid in grasping its importance. For instance, in physics, engineers might use synthetic division to model motion trajectories where polynomial equations are involved. By applying synthetic division, they can compute different parameters quickly, ensuring safer and more efficient designs. Engaging with these practical scenarios will reinforce student learning and highlight the necessity of mastering this method.
Using Technology to Practice Synthetic Division
In today’s technology-driven world, utilizing online courses and educational tools can greatly enhance learning experiences. Many platforms offer interactive modules dedicated to **synthetic division** and **polynomial functions**. A tutor or language-embedded math software can provide personalized assistance, catering to individual learning paces. Engaging with advanced educational platforms will not only simplify the learning process but also help students **improve grades** through consistent practice and assessment.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the basic structure and purpose of synthetic division, particularly how it differs from traditional long division for polynomials.
- Practice the **synthetic division steps** to become proficient in identifying a quotient and the corresponding remainder.
- Recognize the broader applications of synthetic division in real-world situations, enhancing its relevance beyond the classroom.
- Avoid common mistakes related to coefficients and alignment to ensure accurate outcomes.
- Engage with educational resources and problem-solving tools to foster ongoing improvement in algebra skills.
FAQ
1. What is synthetic division, and how does it work?
Synthetic division is a simplified method of dividing polynomials, particularly useful for **linear divisors**. It involves using the coefficients of the polynomials to streamline the division process, allowing faster calculations compared to traditional long division. This approach helps students effectively find remainders and quotients in polynomial expressions.
2. When should I use synthetic division over long division?
Synthetic division is preferred when dividing by a linear polynomial in the form \(x-c\), as it simplifies calculations. For larger, more complicated polynomials, traditional long division may still be necessary, but mastering synthetic division can make polynomial calculations quicker and more efficient overall.
3. How can synthetic division help find polynomial roots?
By applying synthetic division, students can test different values to see if they yield a remainder of zero. If a specific value provides a remainder of zero, then that value is a root of the polynomial, allowing you to factor it further. Utilizing this method aids in finding all **roots** of a polynomial without excessive calculations.
4. What are some common errors made during synthetic division?
Common errors include misalignment of coefficients, neglecting negative signs, and incorrect arithmetic during the calculation of the **remainder**. Paying close attention to detail and being methodical in following the steps will help prevent these mistakes, leading to more successful applications of synthetic division.
5. How can I improve my skills in synthetic division?
Regular practice with diverse **practice problems** is key in improving your skills. Utilize educational resources, online tutorials, structured math courses, or engage in study groups to compare methods and enhance your understanding. Additionally, technology-assisted learning can provide personalized feedback and support to reinforce foundational skills.
6. Is there a relationship between synthetic division and polynomial functions?
Yes, synthetic division is intrinsically linked to polynomial functions as it allows for the **evaluation** of polynomials and the determination of their behavior over specific intervals. By mastering this technique, students can better understand polynomial relationships, transformations, and roots, streamlining their studies in algebra.
7. Can synthetic division be applied in real-world problem-solving?
Absolutely! Synthetic division can model various real-world scenarios, such as calculating trajectories in physics or financial forecasting in economics. As mathematical tools become increasingly vital in professional fields, harnessing synthetic division will enhance problem-solving techniques across disciplines.